A Novel Fluoroscopic Approach to Assessing Patient Positioning in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Accuracy and the Influence of Body Mass Index
Authors: Anton Lambers, Robert Jennings, Andrew Bucknill
Site: Royal Melbourne Hospital, VIC
Proper positioning of the pelvis during Total Hip Replacement (THR) is critical to ensure accurate prosthesis placement when doing conventional (non-technology assisted) THR, as components are inserted under the assumption the patient is positioned perfectly square to the operating table.
This study, conducted by Dr Lambers and colleagues on 37 patients undergoing THA, evaluated a novel method of positioning assessment using X-rays and investigated how body mass index (BMI) affects positioning accuracy.
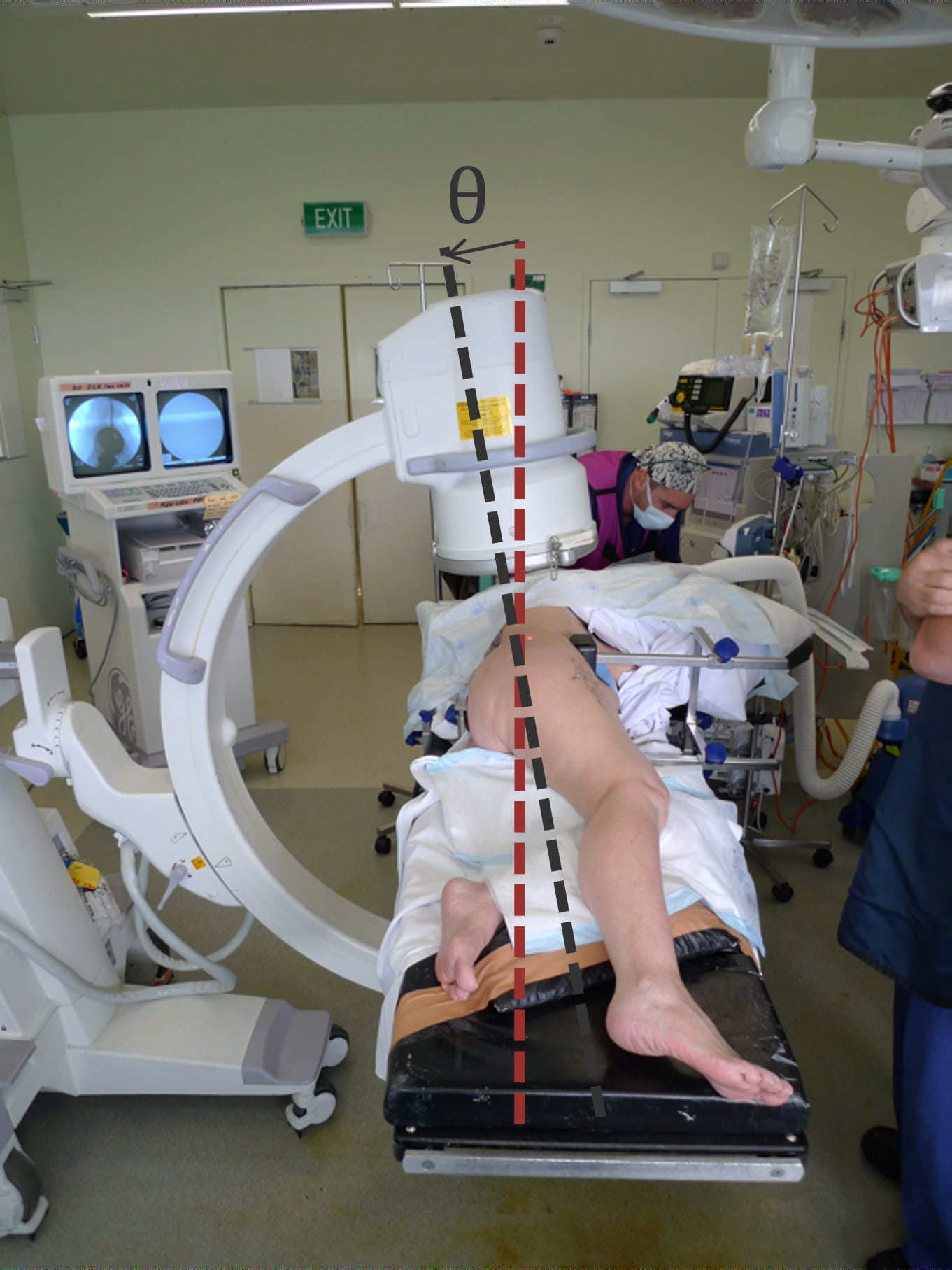
Patients were placed in the lateral position for surgery. A side-on X-ray image was captured through the operating table. The imaging device was adjusted in two planes until the patient’s hip sockets overlapped, indicating correct lateral positioning. The degrees of error in positioning and the BMI of each patient were recorded.
The results were surprising, with more than half the patients showing positioning errors of 5 degrees or more in at least one of the two planes assessed. It highlights the prevalence of pelvic malpositioning in THR and underscores how systems such as robotics may decrease inadvertent errors in component positioning.