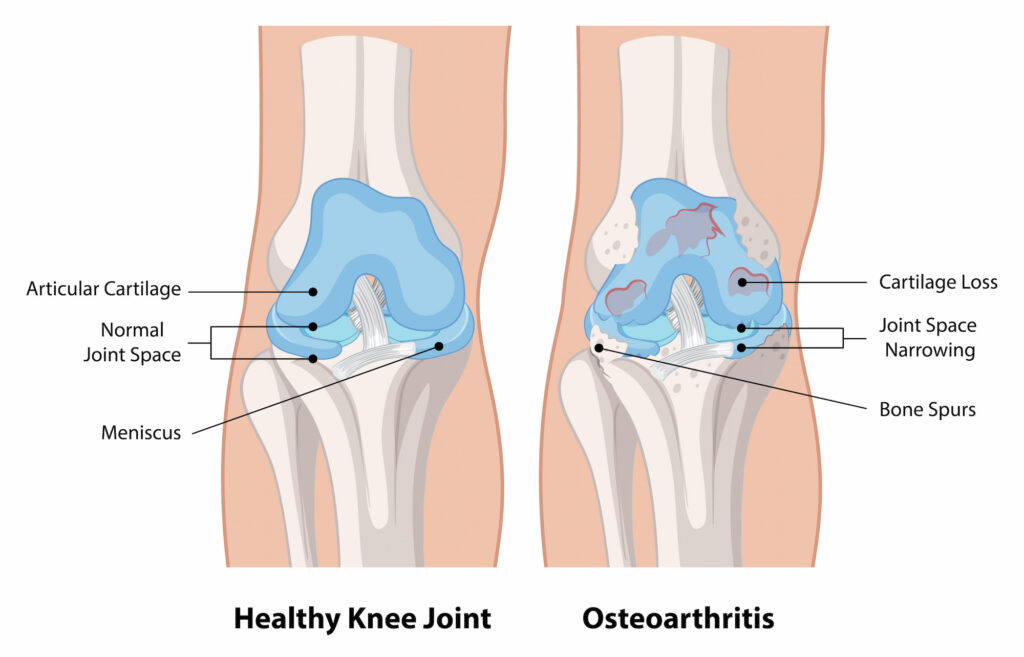
The knee operates as a hinge joint, connecting the thigh bone to the shinbone. It is supported by cartilage that cushions the bones and facilitates smooth movement.
When arthritis develops, this protective cartilage wears down, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Over time, this deterioration can cause the bones to rub against each other, significantly limiting mobility and impacting daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or getting out of a chair.
The most common type of knee arthritis is osteoarthritis, which results from cartilage’s natural wear and tear. Other forms include inflammatory arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or ankylosing spondylitis) and post-traumatic arthritis, which may develop after an injury.
What causes knee arthritis?
Knee arthritis arises due to a combination of factors, some of which are preventable, while others are outside your control. Key causes include:
- Previous knee injuries, such as ligament tears or fractures, can disrupt the joint’s stability and lead to arthritis over time
- A family history of arthritis increases your likelihood of developing the condition, as it may influence joint structure and cartilage strength
- Aging causes wear and tear on the knee joint, making arthritis more common as you grow older
- Excess weight can stress the knee, accelerating cartilage wear and contributing to the early onset of arthritis
What symptoms would I notice?
Knee arthritis symptoms vary depending on the severity of the condition but typically include:
- You may feel pain in or around the knee joint, often accompanied by swelling, particularly after activity or prolonged periods of rest
- The knee may feel stiff, especially in the morning or after sitting for extended periods. Over time, everyday movements like squatting or bending can become increasingly challenging.
- You might notice popping, clicking, or grinding sounds (crepitus) as the bones rub together during movement.
- The knee may feel like it could buckle or give out, making it difficult to bear weight or maintain balance.
How is knee arthritis diagnosed?
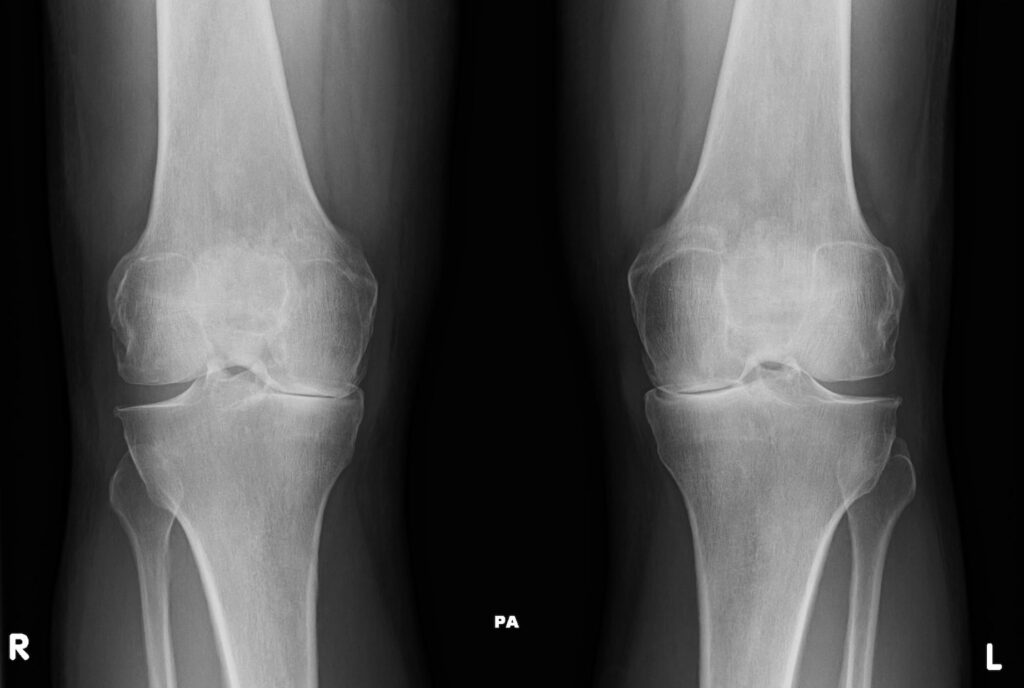
A diagnosis begins with an evaluation by your GP, who will examine the knee for signs of swelling, tenderness, or limited movement. Imaging tests like X-rays can reveal joint damage, loss of cartilage, or bone spurs indicative of arthritis.
Rarely, additional tests such as MRI, CT scans, or blood tests may be recommended to rule out other conditions or confirm a diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis.
Treatment options for knee arthritis
Treatment approaches vary depending on the severity of arthritis and your individual needs. Most cases start with non-operative methods, progressing to surgical options only when necessary.
Non-operative treatments
- Gentle, low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling can strengthen the muscles around the knee, reducing pain and improving stability
- Reducing body weight alleviates stress on the knee, slowing the progression of arthritis and easing discomfort
- Avoiding high-impact activities, using supportive footwear, or employing walking aids like canes can help protect the knee.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol or anti-inflammatory medications can reduce symptoms. Corticosteroid injections may be administered for temporary relief
- Avoiding smoking and ensuring you have a balanced diet can support overall joint health
The Australian Orthopaedic Association has information for patients to assist with how to manage with hip or knee arthritis whilst awaiting surgery, which can be accessed below. The NHS (UK) also has a guide which can help you to make an informed decision about your treatment which is accessible below.
Operative treatment:
When non-surgical options fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered.
Operative treatment options include:
- Knee replacement: This is the most common procedure and involves replacing the damaged joint surfaces with artificial components, restoring mobility and reducing pain. This can be a partial (some surfaces) or total (all surfaces) knee replacement, and Dr Lambers will use a robotic system to ensure accurate placement of the implants.
- Osteotomy: cutting the bone and realigning it to move weight through the side of the knee that has healthy cartilage. This is considered in active patients under 60 years old who are not overweight and still have good movement with arthritis that only affects one side of the knee joint. It is an alternative to replacement surgery in a small group of suitable patients.
Surgery is highly effective for severe arthritis and can dramatically improve quality of life. Dr Lambers will guide you through the process, discussing the benefits, risks, and recovery expectations. Read more about total and partial knee replacements and recovery from surgery below:
Managing knee arthritis with Dr Lambers
While knee arthritis can be challenging, many individuals successfully manage their symptoms with conservative treatments. If your symptoms continue despite these efforts, your GP may refer you to Dr Lambers.
With a personalised approach, Dr Lambers can help you explore advanced treatment options, including surgery if appropriate, to restore function and improve your quality of life.