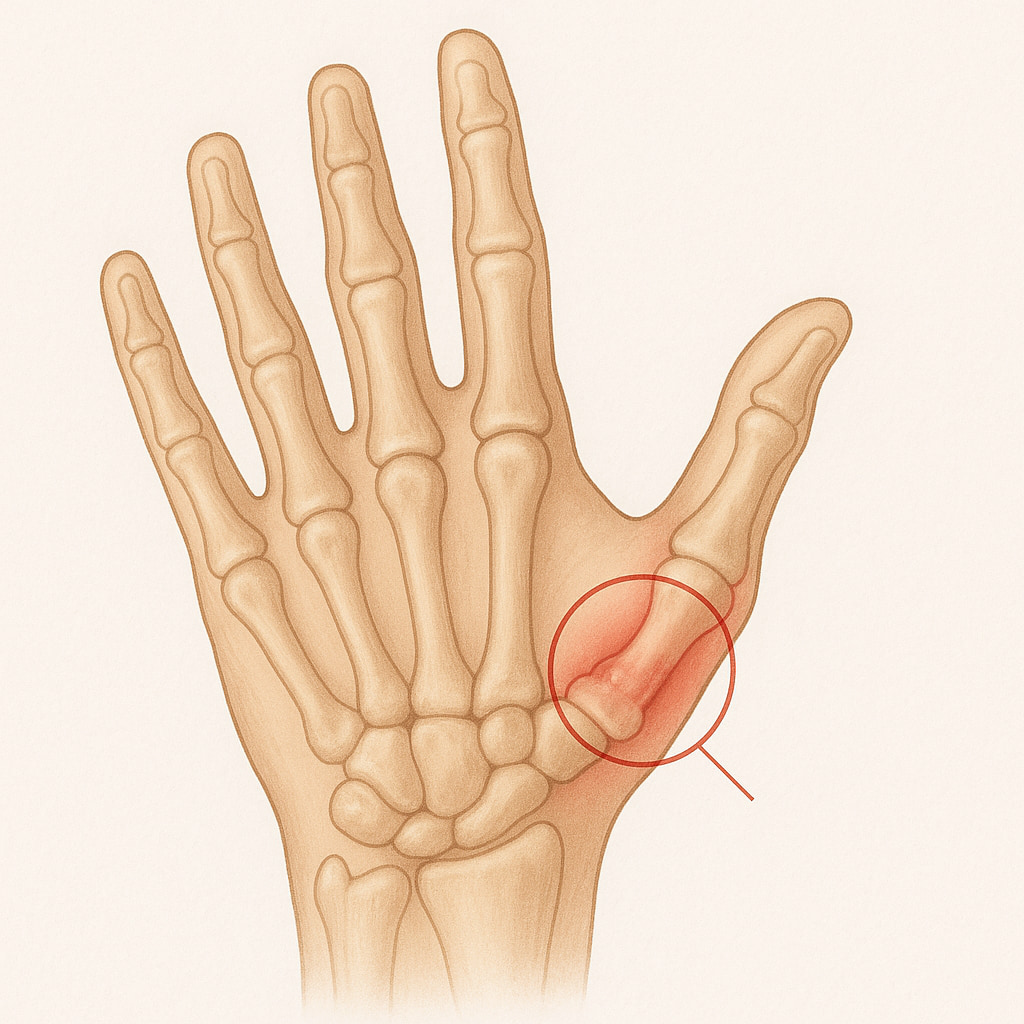
Base of thumb arthritis, also known as carpometacarpal (CMC) arthritis, is a common condition, especially in older adults. It occurs when the cartilage in the joint at the base of the thumb wears down, causing pain and stiffness.
The CMC joint is where the thumb meets the wrist, and as the cartilage deteriorates, the bones rub against each other, leading to inflammation and discomfort. This condition can impact your ability to perform simple tasks such as gripping, pinching, or turning keys.
What causes base of thumb arthritis?
- Wear and tear of cartilage, which naturally happens as we age
- The risk of developing arthritis increases, particularly after the age of 40
- Women are more likely to develop base of thumb arthritis, especially after menopause, due to hormonal changes that affect soft tissues
- Previous trauma, such as fractures or sprains to the thumb joint, can increase the likelihood of arthritis developing later
- Hereditary conditions, such as joint ligament laxity or malformed joints
- Jobs or activities that put repeated stress on the thumb joint, like heavy lifting or fine motor tasks
What symptoms would I notice?
- Pain at the base of the thumb, often during activities that involve gripping, pinching, or applying force
- Pressing on the base of the thumb may cause pain or discomfort
- Reduced range of motion in the thumb, making it difficult to move the thumb away from the hand or perform tasks that require fine motor control
- Swelling around the joint, especially after use
- In advanced cases, a bump or lump may form at the base of the thumb, and the joint may appear deformed (e.g., the middle thumb joint may hyperextend, causing a zigzag appearance)
How is base of thumb arthritis diagnosed?
Your GP will assess your range of motion, joint tenderness, and any visible deformities or swelling in the thumb. X-rays are often the most effective way to confirm the diagnosis of arthritis. In some cases, further imaging like CT or MRI scans may be needed to assess the joint in greater detail.
Treatment options
There are a variety of treatment options available for base of thumb arthritis, ranging from non-operative methods to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition and your symptoms.
Non-operative treatments
- Avoiding activities that can aggravate the pain can help manage symptoms
- Over-the-counter pain relief to reduce pain and inflammation
- A splint can help support the thumb joint, providing stability and reducing strain, which can be ready made or personalised for you from a hand therapist
- Steroid injections can provide short-term pain relief by reducing inflammation in the joint (repeated injections should be avoided to prevent potential damage to the skin or cartilage)
- Hand therapy may include strengthening exercises, joint mobilisation, and posture correction to help improve function and reduce strain on the thumb joint
Operative treatments
- Trapeziectomy
This involves removing the trapezium bone, which forms part of the arthritic joint. Sometimes, this procedure is combined with a ligament or high strength suture to stabilise the thumb and prevent collapse, which is called a suspensionplasty. Read more about what trapeziectomy surgery and the rehabilitation required afterwards entails below:
- Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis)
This technique involves fusing the bones of the joint together in a position of function. While it provides reliable pain relief, it eliminates any joint movement. It may be considered in young labourers who require strength as more of a priority than movement.
- Osteotomy
This procedure involves cutting and realigning the metacarpal bone next to the CMC joint to relieve pressure and realign the thumb.
- Joint Replacement and Denervation (Nerve Removal) Surgery
Joint replacement and denervation surgery are alternative techniques that are being researched.
Thumb surgery options with Dr Lambers
Dr Anton Lambers has extensive experience in treating base of thumb arthritis and can help guide you through the process of managing this condition when surgical options are deemed necessary. He works closely with each patient to determine the best course of action based on the severity of their symptoms, lifestyle needs, and overall health.